Skin Condition Disease
- Compromised Skin Flap/ Graft
- Necrotising Fasciitis (Flesh Eating Disease)
- Diabetic Foot (Non Healing Wounds)
- Thermal/ Extensive Burns
- Cosmetic Surgery Aftercare
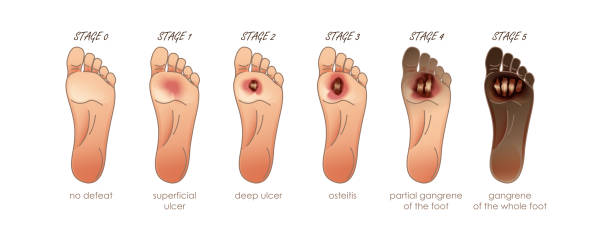
Diabetic Foot (Non Healing Wounds)
Problem wounds are those that don't respond to established medical/surgical management. Problem wounds may include diabetic foot, vascular insufficiency ulcers, non-healing traumatic wounds, and compromised amputation sites. Approximately six million Indians have wounds that do not heal. Chronic leg ulcers: Leg ulcers are unhealed sores or open wounds on the legs. Without treatment, these types of ulcers can keep recurring. This condition is most commonly caused by poor circulation, though it may be attributed to a variety of ailments. The odds of developing leg ulcers increase with age, and they’re often hereditary — in other words, if your parents had leg ulcers, you’re more likely to develop them. Some other causes of leg ulcers are:
- poor blood circulation.
- diabetes.
- hypertension (high blood pressure).
- heart disease.
- high cholesterol.
- kidney disease.
- increased pressure in the legs.
- smoking.
- infections.
- Nerve damage (neuropathy).
- Weakened immune system.
- Narrow arteries.
If they’re treated early, leg ulcers can improve without causing any further complications. They may have diabetes, or other health conditions that increase their risk for chronic or non-healing wounds. Oxygen is required for angiogenesis (which is fostered by the increased oxygen gradient), collagen deposition, Reepithelialization, cellular respiration, and oxidative killing of bacteria. Decreased edema noted following hyperbaric treatment allows better diffusion of oxygen and nutrients through tissues while also relieving pressure on surrounding vessels and structures. In this light, HBO has been used for treating foot ulcers in patients with diabetes, venous and arterial insufficiencies, burn wounds, crush injuries, marginal flaps, and skin grafts. HBOT stimulates and accelerates the healing through the formation of collagen and new blood vessels. Diabetic ulcers and wounds are a great example of wounds that can be treated with hyperbaric oxygen. Research has shown a significant decrease ion amputation rates when using hyperbaric oxygen particularly in patients where surgery is not an option. HBOT can often reverse the damage and effects of poor circulation and help avoid amputation. HBOT promotes growth of new blood vessels (neovascularization). New vasculature for healing needs a supporting structure of collagen. The collagen production and incorporation process needs oxygen. Increased oxygen tension allows greater capillary oxygen diffusion distances and increases oxygen-dependent killing of anaerobes by leukocytes. HBOT is appropriate with many of the other adjunct therapies that help in wound healing.